Fibre & Fabric
· Fibers are thread-like strands. It is very thin, from which fabrics (or cloths) are made. Examples of fibers are wool, silk, cotton, jute, flax, nylon, polyester and polyacrylic.
Animal fibres — wool and silk
· Wool is obtained from goat, sheep, yak and some other animals. The wool-yielding animals bear hair on their body.
· Wool is common in Tibet and Ladakh. Mohair wool is taken from Angora goats found in hilly regions such as Jammu and Kashmir.
· Wool is also obtained from goat hair. The Kashmiri goat possesses a very soft underfur. Which is used to woven into fine shawls called Pashmina shawls.
· The fur (hair) found on the body of the camel is also used as wool. Llama and Alpaca, found in South America, also yield wool.
· For obtaining wool, sheep are reared. Their hair is cut first and then processed into wool.
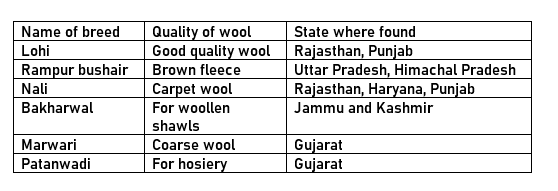
· Sheep are reared in many parts of our country for wool such as Jammu & Kashmir, Uttaranchal, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, or the plains of Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
· The processing of fibre into wool can be represented as follows: Shearing → Scouring → Sorting → Cleaning of burrs→ Rolling Dyeing
SILK
· Silk fibers are also animal fibers. Silkworms spin the ‘silk fibers’.
· Sericulture is the process of rearing silkworms for obtaining silk.
· Female silk moth lays eggs, from which hatch larvae which are called caterpillars or silkworms.
· The female silk moth delivers eggs on the mulberry leaves. Further, eggs are hatched into very small larvae within a week called silkworms or caterpillars. The silkworms feed on the leaves of mulberry tree and grow bigger in size.
· pupa is the next stage of development of silkworm (or caterpillar).
· It moves its head from side to side. During the course of movement of head, the silkworm secrets fiber. which is made of protein. It hardens on exposure to air and becomes silk fiber (or silk thread). Soon the caterpillar completely covers itself by silk fibers and turns into a pupa.
· This covering is known as cocoon.
· The silkworm continues to develop in the form of pupa inside the cocoon to form the silk moth.
· Silk fibers are used for weaving silk cloth.
· The most common silk moth is mulberry.
· The silk fiber obtained from the cocoon of this moth is soft, lustrous and elastic and can be dyed in beautiful colors.
Rearing silkworms:
· A female silk moth lays hundreds of eggs at a time.




